
Covers Ancient America (before 1492) through the Trump administration.
- Subject:
- History
- U.S. History
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Provider:
- Lumen Learning
- Author:
- Boundless
- Date Added:
- 07/13/2021

Covers Ancient America (before 1492) through the Trump administration.
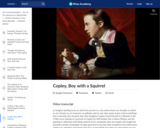
This art history video discussion examines John Singleton Copley's "A Boy with a Flying Squirrel" (Henry Pelham), 1765, 77.15 x 63.82 cm / 30-3/8 x 25-1/8 inches (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston).

The Lawrence Textile Strike was a public protest mainly of immigrant workers from several countries, including Austria, Belgium, Cuba, Canada, France, England, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Russia, Scotland, Spain, Syria, and Turkey. According to the 1910 census, 65% of mill workers (many of whom eventually struck) lived in the United States for less than 10 years; 47% for less than five years. Prompted by a wage cut, the walkout spread quickly from mill to mill across the city. Strikers defied the assumptions of conservative trade unions within the American Federation of Labor that immigrant, largely female and ethnically diverse workers could not be organized. The Lawrence strike is referred to as the Bread and Roses strike and The Strike for Three Loaves." The first known source to do so was a 1916 labor anthology, The Cry for Justice: An Anthology of the Literature of Social Protest by Upton Sinclair. Prior to that, the slogan, used as the title of a 1911 poem by James Oppenheim, had been attributed to Chicago Women Trade Unionists. It has also been attributed to socialist union organizer Rose Schneiderman. James Oppenheim claimed his seeing women strikers in Lawrence carrying a banner proclaiming We Want Bread and Roses Too inspired the poem, Bread and Roses. The poem, however, was written and published in 1911 prior to the strike. Later the poem was set to music by Caroline Kohlsaat and then by Mimi Farina. The song and slogan are now important parts of the labor movement and womens movement worldwide. This exhibition was made in collaboration with the Lawrence History Center and the University of Massachusetts Lowell History Department.
This collection uses primary sources to explore school desegregation in Boston. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.
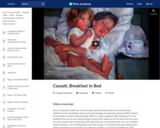
This art history video discussion examines Mary Cassatt's "Breakfast In Bed," 1897 (Huntington Library).

This art history video discussion examines Mary Cassatt's "In the Loge," 1878, oil on canvas, 81.28 x 66.04 cm / 32 x 26 inches (Museum of Fine Arts, Boston).
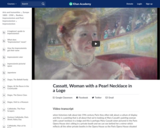
This art history video discussion examines Mary Cassatt's "Woman with a Pearl Necklace in a Loge," 1879, oil on canvas, 32 x 23-1/2 inches or 81.3 x 59.7 cm (Philadelphia Museum of Art).
In twenty-first century American society, childhood is popularly understood as a time of innocence, learning, and play. At the end of the nineteenth century, however, children made up part of the countrys workforce, and labored on farms and in factories. When they were not working, they enjoyed great independence in leisure activitiesbe it in a loud city street or a peaceful country lake. Often, children were far from adult supervision. Reformers during the Progressive Era period of social activism and political reform across the United States between the 1890s and 1920s took a great interest in child welfare. Through organizations and legislation, they sought to define what a happy and healthy childhood should be in the modern age. Immersion in nature was central to what the Progressives prescribed, and childrens organizations and camps offered a suitable combination of supervision and open spaces. The formula for a healthy childhood was further refined in postwar America. Children were given a distinct place in the family and home, as well as within the consumer market with the emergence of teenage culture and buying power. This exhibition was created as part of the DPLA's Public Library Partnerships Project by collaborators from the Digital Library of Georgia and Georgia's public libraries.
This course surveys the social science literature on civil war. Students will study the origins of civil war, discuss variables that affect the duration of civil war, and examine the termination of conflict. This course is highly interdisciplinary and covers a wide variety of cases.

This art history video discussion examines Claes Oldenburg's "Floor Cake," Synthetic polymer paint and latex on canva filled with foam rubber and cardboard boxes, 58.375 x 114.25 x 58.375 in. (148.2 x 290.2 x 148.2 cm) 1962 (MoMA).

In this activity students will learn about how groups without political power—African Americans, women, and working-class men—sought to expand their political power in the Revolutionary era. Students will analyze primary sources to determine the methods by which non-voting groups made their claims on being part of "We the People".

In this lesson students read a description of a slave's walk through colonial New York City and determine which laws he broke and which laws he followed. Students then write a journal entry from the perspective of either a slave or a slaveowner reacting to colonial New York's slave codes.
This collection uses primary sources to explore religion during the Colonial period of US History. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.
This collection uses primary sources to explore the motivations and realities behind life in the American colonies. Digital Public Library of America Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop their critical thinking skills and draw diverse material from libraries, archives, and museums across the United States. Each set includes an overview, ten to fifteen primary sources, links to related resources, and a teaching guide. These sets were created and reviewed by the teachers on the DPLA's Education Advisory Committee.
#2: Settlers Music#3: History of the song Yankee Doodle.

In this activity students read a list of laws regulating Africans and African Americans and a servant's indenture contract from colonial New York. Then students find evidence in the primary sources to support a series of statements about the differences between slaves and servants in the period. This activity includes scaffolds and vocabulary support for students with literacy challenges.

CSDE Model Curricula Quick Start GuideThe African American/Black and Puerto Rican/Latino Course of Studies is a one credit, year-long elective in which students will consider the scope of African American/Black and Puerto Rican/ Latino contributions to U.S. history, society, economy, and culture. It utilizes Connecticut’s Social Studies Framework themes and inquiry-based approach already familiar to social studies teachers to deliver a content rich and personalized learning experience.The course is an opportunity for students to explore accomplishments, struggles, intersections, perspectives, and collaborations of African American/Black and Puerto Rican/Latino people in the U.S. Students will examine how historical movements, legislation, and wars affected the citizenship rights of these groups and how they, both separately and together, worked to build U.S. cultural and economic wealth and create more just societies in local, national, and international contexts.Coursework will provide students with tools to identify historic and contemporary tensions around race and difference; map economic and racial disparities over time; strengthen their own identity development; and address bias in their communities. This course will contribute to the critical consciousness and civic-mindedness competencies of a twenty-first century graduate, and ultimately facilitate students’ interest in pursuing further ethnic, anthropology, or human rights studies in the future.

Developed By: Dan Broyld and Paquita Jarman-Smith The journey to abolish slavery in the United States was a battle that progressed gradually over time. The unit explores: the individuals, groups, and schools of thought that contributed to the movement. The subsections of the unit will move through the topics of Black survival and resistance to enslavement and emancipation using the Gradualist, Militant, Early and Late Political Periods, and the Civil War. Students will also examine “Free” Black communities, Slave Narratives, Negro Spirituals, folklores, newspapers, pamphlets, and speeches that Blacks and abolitionists employed to precipitate change. Themes of resistance and agency will be examined.In this unit, students will:• Examine how Africans and African descendants worked individually and collectively to spark revolutionary change to their existence; and• Explore various perspectives of enslavement from free and enslaved Africans.Compelling Questions: When is resistance and/or revolution justified/glorified/condemned? How effective were the actions of abolitionists and the slave rebellions of this period? Are individual contributions or collective efforts more effective in actualizing social change?
Big Ideas/Topics to be Addressed, including Key Concepts and Terms Ways slaves resisted Denmark Vesey-Slave Revolt Role of Black Churches in Slave Resistance The Haitian Revolution inspired the abolition movement in the U.S. Role of Abolitionists Black Communities in CT Black Press Vocabulary: Slave Resistance, Abolition, Gradualist Period, Negro Spirituals
Big Ideas/Topics to be Addressed, including Key Concepts and Terms Nat Turner Underground Railroad Harriet Tubman La Amistad (1839-1841) Vocabulary: Militant, sectionalism, defining race riot