
- Subject:
- Applied Science
- Biology
- Life Science
- Material Type:
- Module
- Author:
- OpenStax College
- Date Added:
- 07/18/2021


By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe what must occur for plant fertilizationExplain cross-pollination and the ways in which it takes placeDescribe the process that leads to the development of a seedDefine double fertilization

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the two stages of a plant’s lifecycleCompare and contrast male and female gametophytes and explain how they form in angiospermsDescribe the reproductive structures of a plantDescribe the components of a complete flowerDescribe the development of microsporangium and megasporangium in gymnosperms


By the end of this section, you will be able to:Understand the nutritional adaptations of plantsDescribe mycorrhizaeExplain nitrogen fixation
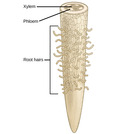
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how plants obtain nutrientsList the elements and compounds required for proper plant nutritionDescribe an essential nutrient

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how soils are formedExplain soil compositionDescribe a soil profile

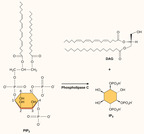
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Explain how the binding of a ligand initiates signal transduction throughout a cellRecognize the role of phosphorylation in the transmission of intracellular signalsEvaluate the role of second messengers in signal transmission
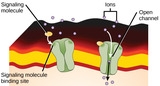
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe four types of signaling found in multicellular organismsCompare internal receptors with cell-surface receptorsRecognize the relationship between a ligand’s structure and its mechanism of action

By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how single-celled yeasts use cell signaling to communicate with one anotherRelate the role of quorum sensing to the ability of some bacteria to form biofilms
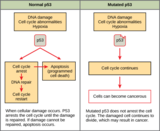
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe how cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell growthUnderstand how proto-oncogenes are normal cell genes that, when mutated, become oncogenesDescribe how tumor suppressors functionExplain how mutant tumor suppressors cause cancer
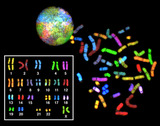
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomesDistinguish between chromosomes, genes, and traitsDescribe the mechanisms of chromosome compaction
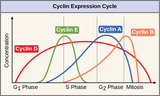
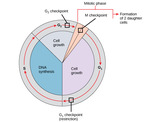
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms both internal and external to the cellExplain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of G1, at the G2/M transition, and during metaphaseDescribe the molecules that control the cell cycle through positive and negative regulation
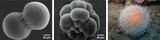
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the process of binary fission in prokaryotesExplain how FtsZ and tubulin proteins are examples of homology
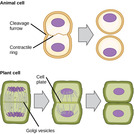
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the three stages of interphaseDiscuss the behavior of chromosomes during karyokinesisExplain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesisDefine the quiescent G0 phase
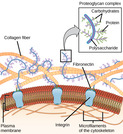
By the end of this section, you will be able to:Describe the extracellular matrixList examples of the ways that plant cells and animal cells communicate with adjacent cellsSummarize the roles of tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and plasmodesmata